China Tops Global Rankings in Computer Vision Surveillance Research: CSET
A recent study from the Center for Security and Emerging Technology (CSET) has shed light on China's significant lead in the research of AI-related surveillance technologies. The report, titled **Trends in AI Research for the Visual Surveillance of Populations**, delves into how China's research sector is producing a disproportionate amount of work in three core areas of AI surveillance: person re-identification (REID), crowd counting, and spoofing detection. These technologies are crucial for identifying individuals, monitoring crowds, and detecting attempts to bypass identification systems, respectively.
The study, conducted by Ashwin Acharya, Max Langenkamp, and James Dunham, analyzed a vast dataset of scientific papers published between 2015 and 2019. Their findings indicate that China's researchers are not only leading in these specific surveillance technologies but are also increasingly contributing to the broader field of computer vision, outpacing Western publication rates.
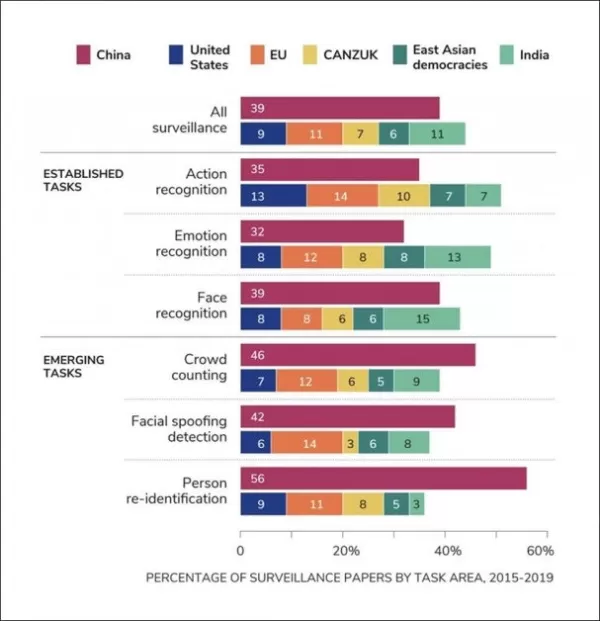 China's clear lead in research initiatives into more controversial sub-sectors of computer vision research, chiefly related to surveillance. Source: https://cset.georgetown.edu/wp-content/uploads/Surveillance-in-the-CV-Literature.pdf
China's clear lead in research initiatives into more controversial sub-sectors of computer vision research, chiefly related to surveillance. Source: https://cset.georgetown.edu/wp-content/uploads/Surveillance-in-the-CV-Literature.pdf
China's Focus on Human-Facing Computer Vision
The report highlights that a significant portion of Chinese research focuses on human-facing computer vision tasks, such as emotion recognition, face recognition, and action recognition. These technologies, while often used for benign purposes like social media photo tagging, could also be employed by governments for more repressive surveillance activities.
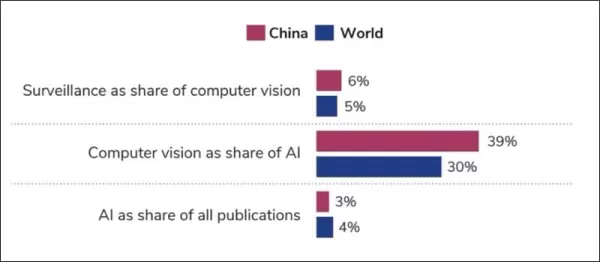
The authors note that while visual surveillance research accounts for less than 10% of all computer vision research during the study period, China's dominance in both computer vision and visual surveillance research is undeniable. They state, **‘Researchers with Chinese institutional affiliations were responsible for more than one third of publications in both computer vision and visual surveillance research. This makes China by far the most prolific country in both areas. Chinese researchers’ share of global visual surveillance research is growing at a similar rate to their share of computer vision research.'**
Limitations and Broader Context
The study focused solely on English language scientific papers, which the authors acknowledge limits their findings. They suggest that including non-English publications, especially from China, might reveal even more extensive research efforts. Additionally, incorporating patent data, camera deployment, and relevant government policies could further illustrate China's lead in these fields.
The authors used Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques, specifically the SciREX model trained on data from Papers With Code, to analyze over 100 million publications across six academic datasets. The SciBERT classifier, trained on Arxiv preprints, helped identify computer vision papers within this corpus. However, the reliance on English language documents means the study likely underestimates non-English research output, particularly from China.
Key Findings and Implications
The report found face recognition to be the most recurrent task in visual surveillance research, appearing in over a thousand papers in 2019 alone. Crowd-counting and face-spoofing recognition are also rapidly growing fields. The authors express concern that even seemingly neutral computer vision technologies can contribute to repressive systems. For instance, action recognition can detect 'abnormal behavior' in public spaces, face spoofing can prevent journalists and activists from concealing their identities, and emotion recognition can be used to identify security threats in crowded areas.
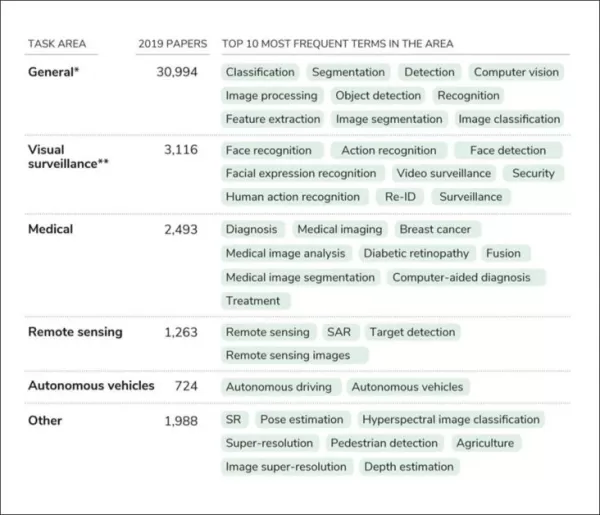 From the paper, the most frequently recurring tasks individuated for the years studied. Cited source is ‘CSET merged corpus. Results generated July 22, 2021'
From the paper, the most frequently recurring tasks individuated for the years studied. Cited source is ‘CSET merged corpus. Results generated July 22, 2021'
The authors conclude that China's share of both computer vision and visual surveillance research has increased over time, while the United States and its allies have maintained a similar level of output. However, the global share of surveillance research from other regions has either remained stable or declined, highlighting China's growing dominance in this area.
This comprehensive study underscores the importance of monitoring global trends in AI and surveillance technology research, particularly given the potential implications for privacy and civil liberties.
**First published 6th January 2022.**
Related article
 Google Cloud Powers Breakthroughs in Scientific Research and Discovery
The digital revolution is transforming scientific methodologies through unprecedented computational capabilities. Cutting-edge technologies now augment both theoretical frameworks and laboratory experiments, propelling breakthroughs across discipline
Google Cloud Powers Breakthroughs in Scientific Research and Discovery
The digital revolution is transforming scientific methodologies through unprecedented computational capabilities. Cutting-edge technologies now augment both theoretical frameworks and laboratory experiments, propelling breakthroughs across discipline
 AI Accelerates Scientific Research for Greater Real-World Impact
Google has consistently harnessed AI as a catalyst for scientific progress, with today's pace of discovery reaching extraordinary new levels. This acceleration has transformed the research cycle, turning fundamental breakthroughs into practical appli
AI Accelerates Scientific Research for Greater Real-World Impact
Google has consistently harnessed AI as a catalyst for scientific progress, with today's pace of discovery reaching extraordinary new levels. This acceleration has transformed the research cycle, turning fundamental breakthroughs into practical appli
 Ethics in AI: Tackling Bias and Compliance Challenges in Automation
As automation becomes deeply embedded across industries, ethical considerations are emerging as critical priorities. Decision-making algorithms now influence crucial aspects of society including employment opportunities, financial services, medical c
Comments (15)
0/200
Ethics in AI: Tackling Bias and Compliance Challenges in Automation
As automation becomes deeply embedded across industries, ethical considerations are emerging as critical priorities. Decision-making algorithms now influence crucial aspects of society including employment opportunities, financial services, medical c
Comments (15)
0/200
![CharlesMartinez]() CharlesMartinez
CharlesMartinez
 April 22, 2025 at 9:04:36 AM EDT
April 22, 2025 at 9:04:36 AM EDT
A liderança da China na pesquisa de vigilância por IA é assustadora, mas fascinante! O relatório da CSET realmente abriu meus olhos para o quão avançados eles estão. Parece algo saído de um filme de ficção científica, mas é a vida real! Talvez devêssemos todos começar a aprender mais sobre isso, hein? 🤔


 0
0
![BillyThomas]() BillyThomas
BillyThomas
 April 22, 2025 at 4:16:56 AM EDT
April 22, 2025 at 4:16:56 AM EDT
El dominio de China en la investigación de vigilancia por IA es un poco aterrador pero también fascinante. El informe de CSET realmente me abrió los ojos sobre lo avanzados que están. ¡Es como algo salido de una película de ciencia ficción, pero es la vida real! Tal vez deberíamos todos empezar a aprender más sobre esto, ¿eh? 🤔


 0
0
![ChristopherAllen]() ChristopherAllen
ChristopherAllen
 April 21, 2025 at 9:12:02 PM EDT
April 21, 2025 at 9:12:02 PM EDT
El liderazgo de China en la investigación de vigilancia con IA es un poco aterrador, pero impresionante. El informe de CSET realmente abre los ojos sobre lo avanzados que están. Es fascinante pero también preocupante. ¡Ojalá hubiera más transparencia sobre cómo se usa esta tecnología! 🤔


 0
0
![JustinAnderson]() JustinAnderson
JustinAnderson
 April 21, 2025 at 4:34:01 PM EDT
April 21, 2025 at 4:34:01 PM EDT
Interesante ver a China liderando en la investigación de vigilancia por IA. El informe es detallado pero un poco demasiado académico para mi gusto. Podría usar más ejemplos del mundo real para hacerlo más relatable. ¡Aún así, es revelador! 👀


 0
0
![RalphSanchez]() RalphSanchez
RalphSanchez
 April 21, 2025 at 11:36:13 AM EDT
April 21, 2025 at 11:36:13 AM EDT
중국이 AI 감시 기술 연구에서 선두를 달리고 있다는 게 흥미로워요. 보고서는 상세하지만, 제 취향에는 조금 학문적이에요. 실제 사례를 더 넣으면 좋겠어요. 그래도 눈 뜨이는 내용이에요! 👀


 0
0
![EricRoberts]() EricRoberts
EricRoberts
 April 21, 2025 at 6:56:48 AM EDT
April 21, 2025 at 6:56:48 AM EDT
중국이 AI 감시 기술 연구에서 세계를 선도하고 있다는 게 놀랍네요! CSET 보고서를 보고 얼마나 발전했는지 알게 되었어요. 마치 SF 영화 같지만, 이게 현실이에요. 이 분야에 대해 더 배워야 할지도 모르겠어요. 😲


 0
0
A recent study from the Center for Security and Emerging Technology (CSET) has shed light on China's significant lead in the research of AI-related surveillance technologies. The report, titled **Trends in AI Research for the Visual Surveillance of Populations**, delves into how China's research sector is producing a disproportionate amount of work in three core areas of AI surveillance: person re-identification (REID), crowd counting, and spoofing detection. These technologies are crucial for identifying individuals, monitoring crowds, and detecting attempts to bypass identification systems, respectively.
The study, conducted by Ashwin Acharya, Max Langenkamp, and James Dunham, analyzed a vast dataset of scientific papers published between 2015 and 2019. Their findings indicate that China's researchers are not only leading in these specific surveillance technologies but are also increasingly contributing to the broader field of computer vision, outpacing Western publication rates.
 China's clear lead in research initiatives into more controversial sub-sectors of computer vision research, chiefly related to surveillance. Source: https://cset.georgetown.edu/wp-content/uploads/Surveillance-in-the-CV-Literature.pdf
China's clear lead in research initiatives into more controversial sub-sectors of computer vision research, chiefly related to surveillance. Source: https://cset.georgetown.edu/wp-content/uploads/Surveillance-in-the-CV-Literature.pdf
China's Focus on Human-Facing Computer Vision
The report highlights that a significant portion of Chinese research focuses on human-facing computer vision tasks, such as emotion recognition, face recognition, and action recognition. These technologies, while often used for benign purposes like social media photo tagging, could also be employed by governments for more repressive surveillance activities.
The authors note that while visual surveillance research accounts for less than 10% of all computer vision research during the study period, China's dominance in both computer vision and visual surveillance research is undeniable. They state, **‘Researchers with Chinese institutional affiliations were responsible for more than one third of publications in both computer vision and visual surveillance research. This makes China by far the most prolific country in both areas. Chinese researchers’ share of global visual surveillance research is growing at a similar rate to their share of computer vision research.'**
Limitations and Broader Context
The study focused solely on English language scientific papers, which the authors acknowledge limits their findings. They suggest that including non-English publications, especially from China, might reveal even more extensive research efforts. Additionally, incorporating patent data, camera deployment, and relevant government policies could further illustrate China's lead in these fields.
The authors used Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques, specifically the SciREX model trained on data from Papers With Code, to analyze over 100 million publications across six academic datasets. The SciBERT classifier, trained on Arxiv preprints, helped identify computer vision papers within this corpus. However, the reliance on English language documents means the study likely underestimates non-English research output, particularly from China.
Key Findings and Implications
The report found face recognition to be the most recurrent task in visual surveillance research, appearing in over a thousand papers in 2019 alone. Crowd-counting and face-spoofing recognition are also rapidly growing fields. The authors express concern that even seemingly neutral computer vision technologies can contribute to repressive systems. For instance, action recognition can detect 'abnormal behavior' in public spaces, face spoofing can prevent journalists and activists from concealing their identities, and emotion recognition can be used to identify security threats in crowded areas.
 From the paper, the most frequently recurring tasks individuated for the years studied. Cited source is ‘CSET merged corpus. Results generated July 22, 2021'
From the paper, the most frequently recurring tasks individuated for the years studied. Cited source is ‘CSET merged corpus. Results generated July 22, 2021'
The authors conclude that China's share of both computer vision and visual surveillance research has increased over time, while the United States and its allies have maintained a similar level of output. However, the global share of surveillance research from other regions has either remained stable or declined, highlighting China's growing dominance in this area.

This comprehensive study underscores the importance of monitoring global trends in AI and surveillance technology research, particularly given the potential implications for privacy and civil liberties.
**First published 6th January 2022.**
 Google Cloud Powers Breakthroughs in Scientific Research and Discovery
The digital revolution is transforming scientific methodologies through unprecedented computational capabilities. Cutting-edge technologies now augment both theoretical frameworks and laboratory experiments, propelling breakthroughs across discipline
Google Cloud Powers Breakthroughs in Scientific Research and Discovery
The digital revolution is transforming scientific methodologies through unprecedented computational capabilities. Cutting-edge technologies now augment both theoretical frameworks and laboratory experiments, propelling breakthroughs across discipline
 AI Accelerates Scientific Research for Greater Real-World Impact
Google has consistently harnessed AI as a catalyst for scientific progress, with today's pace of discovery reaching extraordinary new levels. This acceleration has transformed the research cycle, turning fundamental breakthroughs into practical appli
AI Accelerates Scientific Research for Greater Real-World Impact
Google has consistently harnessed AI as a catalyst for scientific progress, with today's pace of discovery reaching extraordinary new levels. This acceleration has transformed the research cycle, turning fundamental breakthroughs into practical appli
 April 22, 2025 at 9:04:36 AM EDT
April 22, 2025 at 9:04:36 AM EDT
A liderança da China na pesquisa de vigilância por IA é assustadora, mas fascinante! O relatório da CSET realmente abriu meus olhos para o quão avançados eles estão. Parece algo saído de um filme de ficção científica, mas é a vida real! Talvez devêssemos todos começar a aprender mais sobre isso, hein? 🤔


 0
0
 April 22, 2025 at 4:16:56 AM EDT
April 22, 2025 at 4:16:56 AM EDT
El dominio de China en la investigación de vigilancia por IA es un poco aterrador pero también fascinante. El informe de CSET realmente me abrió los ojos sobre lo avanzados que están. ¡Es como algo salido de una película de ciencia ficción, pero es la vida real! Tal vez deberíamos todos empezar a aprender más sobre esto, ¿eh? 🤔


 0
0
 April 21, 2025 at 9:12:02 PM EDT
April 21, 2025 at 9:12:02 PM EDT
El liderazgo de China en la investigación de vigilancia con IA es un poco aterrador, pero impresionante. El informe de CSET realmente abre los ojos sobre lo avanzados que están. Es fascinante pero también preocupante. ¡Ojalá hubiera más transparencia sobre cómo se usa esta tecnología! 🤔


 0
0
 April 21, 2025 at 4:34:01 PM EDT
April 21, 2025 at 4:34:01 PM EDT
Interesante ver a China liderando en la investigación de vigilancia por IA. El informe es detallado pero un poco demasiado académico para mi gusto. Podría usar más ejemplos del mundo real para hacerlo más relatable. ¡Aún así, es revelador! 👀


 0
0
 April 21, 2025 at 11:36:13 AM EDT
April 21, 2025 at 11:36:13 AM EDT
중국이 AI 감시 기술 연구에서 선두를 달리고 있다는 게 흥미로워요. 보고서는 상세하지만, 제 취향에는 조금 학문적이에요. 실제 사례를 더 넣으면 좋겠어요. 그래도 눈 뜨이는 내용이에요! 👀


 0
0
 April 21, 2025 at 6:56:48 AM EDT
April 21, 2025 at 6:56:48 AM EDT
중국이 AI 감시 기술 연구에서 세계를 선도하고 있다는 게 놀랍네요! CSET 보고서를 보고 얼마나 발전했는지 알게 되었어요. 마치 SF 영화 같지만, 이게 현실이에요. 이 분야에 대해 더 배워야 할지도 모르겠어요. 😲


 0
0