Streamline Patching, Slash Exposure: Why Ring Deployment is Critical for Enterprise Security
Unpatched systems are a critical vulnerability. Over half (57%) of cyberattack victims report that applying available patches could have prevented breaches, yet nearly one-third fail to act, amplifying risks.
Research from Ponemon indicates organizations now average 43 days to detect cyberattacks post-patch release, up from 36 days last year. The Verizon 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report notes a 180% surge in attackers exploiting vulnerabilities from 2023 to 2024.
Manual or semi-automated patching is increasingly overwhelming, often sidelined by IT teams under constant pressure.
Dependence on manual or partially automated patching is seen as overly time-intensive, pushing it lower on priority lists. An Ivanti study reveals 71% of IT and security professionals find patching complex and cumbersome.
Patching Delays Invite Disaster
Cybercriminals relentlessly target legacy Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs), some over a decade old.
Attackers’ growing success with vulnerabilities from 2010–2019, with 76% of ransomware exploits tied to these CVEs, highlights their ability to weaponize old flaws. Misalignment between IT and security teams exacerbates delays, with 27% lacking unified patch strategies and nearly a quarter clashing over schedules. Automating patch management helps resolve these conflicts, streamlining workflows.
Gartner’s recent report, “We’re Not Patching Our Way Out of Vulnerability Exposure,” notes that enterprises typically patch 90% of desktops in two to four weeks, 80% of Windows servers in six weeks, and just 25% of Oracle Databases within six months. It warns, “No organization is outpacing threat actors at scale.”
Ring Deployment: Scalable, Proactive Protection
Every unpatched endpoint is a potential entry point for attackers. Enterprises are struggling to keep up, emboldening cybercriminals.
Patching complexity has grown significantly, overwhelming manual efforts. Initially used in Microsoft-centric networks, ring deployment has expanded to on-premise and cloud-based systems. This phased, automated approach minimizes attacker opportunities and reduces breach risks.
Ring deployment implements patches in controlled stages:
- Test Ring (1%): IT teams verify patch stability.
- Early Adopter Ring (5–10%): A wider group tests real-world performance.
- Production Ring (80–90%): Full rollout follows confirmed stability.
Ivanti’s ring deployment solution empowers security teams with precise control over patch timing, systems, and update sequences, minimizing disruptions and risks.
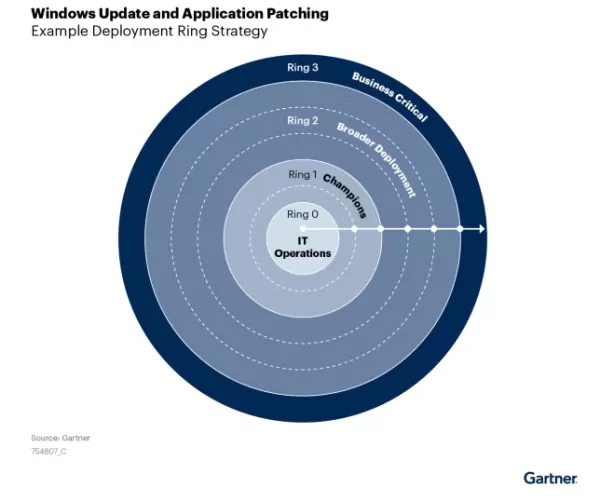
Gartner’s ring deployment model scales patches from internal IT outward, ensuring validation and minimizing risks. Source: Gartner, “Modernize Windows and Third-Party Application Patching,” p. 6. Ring Deployment Slashes MTTP, Ends Patching Chaos
Using outdated vulnerability scores to guide patch strategies heightens breach risks as teams struggle with growing backlogs. This creates a relentless cycle, with attackers exploiting unprotected legacy CVEs.
Gartner’s “Modernize Windows and Third-Party Application Patching” report underscores the failure of traditional methods. In contrast, ring deployment delivers results, achieving a 99% patch success rate within 24 hours for up to 100,000 PCs.
In a VentureBeat interview, Tony Miller, Ivanti’s VP of enterprise services, stated, “Ivanti Neurons for Patch Management and ring deployment are key to our Customer Zero journey.” He noted the company’s internal use of its tools provides rapid feedback and insight into customer challenges.
Miller added, “Our internal testing of ring deployment has shown benefits in risk-based patch deployment, ensuring updates don’t disrupt productivity—a major hurdle for IT teams.”
VentureBeat also interviewed Jesse Miller, SVP and IT director at Southstar Bank, about Ivanti’s AI-driven Vulnerability Risk Rating (VRR), which recalibrates based on real-time threat intelligence and exploit activity.
Jesse Miller emphasized, “Relying solely on CVSS scores is outdated. Effective prioritization considers current events, industry, and environment. We’re making smarter decisions by enhancing, not ignoring, CVSS.”
He further noted, “We prioritize zero-day and high-risk patches, tackling actively exploited vulnerabilities first to shrink our attack surface quickly.”
By integrating ring deployment with dynamic VRR, Ivanti Neurons orchestrates phased patch rollouts, drastically cutting Mean-Time-to-Patch (MTTP) and reducing exposure windows.
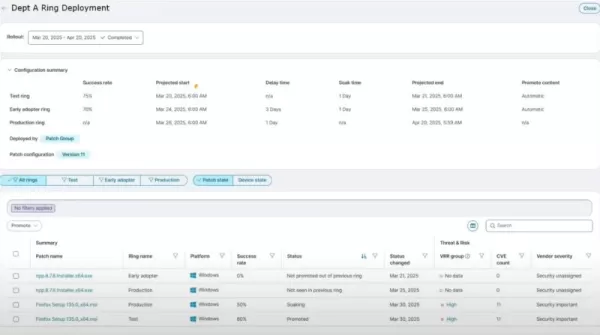
Ivanti Neurons’ interface tracks deployment rings, success metrics, and patching progress for operational clarity. Source: Ivanti Neurons Ivanti Neurons vs. Microsoft Autopatch, Tanium, ServiceNow: Strengths and Limitations
Comparing enterprise patch management solutions reveals distinct differences among Microsoft Autopatch, Tanium, ServiceNow, and Ivanti Neurons.
Microsoft Autopatch uses ring deployment but is limited to Windows and Microsoft 365 environments. Ivanti Neurons supports a wider range, including Windows, macOS, Linux, and third-party applications, ideal for diverse infrastructures.
Tanium excels in endpoint visibility and reporting but requires significant resources, suiting larger enterprises. ServiceNow shines in workflow automation and IT service integration but often needs customization for patching.
Ivanti Neurons stands out with dynamic risk assessments, phased ring deployments, and automated workflows in one platform, addressing visibility gaps, complexity, and prioritization challenges with real-time dashboards.
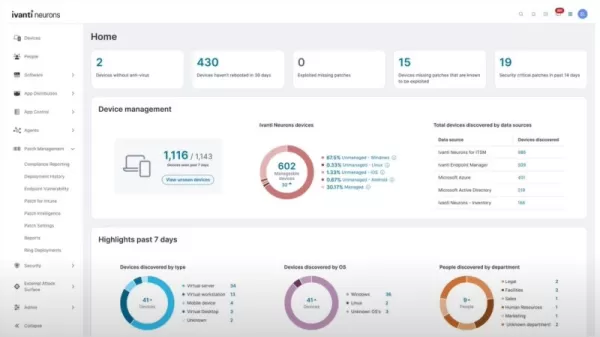
Ivanti Neurons delivers real-time patch status, vulnerability insights, and risk metrics for ongoing visibility. Source: Ivanti Neurons Turning Patch Management into a Strategic Asset
Patching alone isn’t enough to eliminate vulnerabilities. Gartner emphasizes integrating endpoint protection, multifactor authentication, and network segmentation to bolster security beyond patching.
Pairing ring deployment with zero-trust controls enables IT teams to minimize exposure windows and manage risks effectively.
Ivanti’s ring deployment integrates real-time risk assessments, automated remediation, and threat management, aligning patch management with business resilience. Built into Ivanti Neurons, it provides scalable, real-time risk visibility.
Conclusion: Combining ring deployment with prioritization tools and compensating controls transforms patch management into a proactive, strategic advantage.
Related article
 Vast Data Targets $25B Valuation in Latest Funding Round
Vast Data, a provider of AI-optimized data storage solutions, is seeking to raise funds at a significantly higher valuation.Earlier this year, the nine-year-old firm aimed for a $25 billion valuation,
Vast Data Targets $25B Valuation in Latest Funding Round
Vast Data, a provider of AI-optimized data storage solutions, is seeking to raise funds at a significantly higher valuation.Earlier this year, the nine-year-old firm aimed for a $25 billion valuation,
 Kawtco L815 AI Voice Recorder: Unboxing and Comprehensive User Guide
In today’s fast-moving world, a dependable voice recorder is essential. The Kawtco L815 AI Voice Recorder delivers cutting-edge AI features, making it ideal for diverse needs. From capturing phone cal
Kawtco L815 AI Voice Recorder: Unboxing and Comprehensive User Guide
In today’s fast-moving world, a dependable voice recorder is essential. The Kawtco L815 AI Voice Recorder delivers cutting-edge AI features, making it ideal for diverse needs. From capturing phone cal
 OpenAI Commits to Fixes After ChatGPT's Overly Agreeable Responses
OpenAI plans to revise its AI model update process for ChatGPT after an update caused excessively sycophantic responses, prompting widespread user feedback.Last weekend, following an update to GPT-4o,
Comments (0)
0/200
OpenAI Commits to Fixes After ChatGPT's Overly Agreeable Responses
OpenAI plans to revise its AI model update process for ChatGPT after an update caused excessively sycophantic responses, prompting widespread user feedback.Last weekend, following an update to GPT-4o,
Comments (0)
0/200
Unpatched systems are a critical vulnerability. Over half (57%) of cyberattack victims report that applying available patches could have prevented breaches, yet nearly one-third fail to act, amplifying risks.
Research from Ponemon indicates organizations now average 43 days to detect cyberattacks post-patch release, up from 36 days last year. The Verizon 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report notes a 180% surge in attackers exploiting vulnerabilities from 2023 to 2024.
Manual or semi-automated patching is increasingly overwhelming, often sidelined by IT teams under constant pressure.
Dependence on manual or partially automated patching is seen as overly time-intensive, pushing it lower on priority lists. An Ivanti study reveals 71% of IT and security professionals find patching complex and cumbersome.
Patching Delays Invite Disaster
Cybercriminals relentlessly target legacy Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs), some over a decade old.
Attackers’ growing success with vulnerabilities from 2010–2019, with 76% of ransomware exploits tied to these CVEs, highlights their ability to weaponize old flaws. Misalignment between IT and security teams exacerbates delays, with 27% lacking unified patch strategies and nearly a quarter clashing over schedules. Automating patch management helps resolve these conflicts, streamlining workflows.
Gartner’s recent report, “We’re Not Patching Our Way Out of Vulnerability Exposure,” notes that enterprises typically patch 90% of desktops in two to four weeks, 80% of Windows servers in six weeks, and just 25% of Oracle Databases within six months. It warns, “No organization is outpacing threat actors at scale.”
Ring Deployment: Scalable, Proactive Protection
Every unpatched endpoint is a potential entry point for attackers. Enterprises are struggling to keep up, emboldening cybercriminals.
Patching complexity has grown significantly, overwhelming manual efforts. Initially used in Microsoft-centric networks, ring deployment has expanded to on-premise and cloud-based systems. This phased, automated approach minimizes attacker opportunities and reduces breach risks.
Ring deployment implements patches in controlled stages:
- Test Ring (1%): IT teams verify patch stability.
- Early Adopter Ring (5–10%): A wider group tests real-world performance.
- Production Ring (80–90%): Full rollout follows confirmed stability.
Ivanti’s ring deployment solution empowers security teams with precise control over patch timing, systems, and update sequences, minimizing disruptions and risks.

Ring Deployment Slashes MTTP, Ends Patching Chaos
Using outdated vulnerability scores to guide patch strategies heightens breach risks as teams struggle with growing backlogs. This creates a relentless cycle, with attackers exploiting unprotected legacy CVEs.
Gartner’s “Modernize Windows and Third-Party Application Patching” report underscores the failure of traditional methods. In contrast, ring deployment delivers results, achieving a 99% patch success rate within 24 hours for up to 100,000 PCs.
In a VentureBeat interview, Tony Miller, Ivanti’s VP of enterprise services, stated, “Ivanti Neurons for Patch Management and ring deployment are key to our Customer Zero journey.” He noted the company’s internal use of its tools provides rapid feedback and insight into customer challenges.
Miller added, “Our internal testing of ring deployment has shown benefits in risk-based patch deployment, ensuring updates don’t disrupt productivity—a major hurdle for IT teams.”
VentureBeat also interviewed Jesse Miller, SVP and IT director at Southstar Bank, about Ivanti’s AI-driven Vulnerability Risk Rating (VRR), which recalibrates based on real-time threat intelligence and exploit activity.
Jesse Miller emphasized, “Relying solely on CVSS scores is outdated. Effective prioritization considers current events, industry, and environment. We’re making smarter decisions by enhancing, not ignoring, CVSS.”
He further noted, “We prioritize zero-day and high-risk patches, tackling actively exploited vulnerabilities first to shrink our attack surface quickly.”
By integrating ring deployment with dynamic VRR, Ivanti Neurons orchestrates phased patch rollouts, drastically cutting Mean-Time-to-Patch (MTTP) and reducing exposure windows.

Ivanti Neurons vs. Microsoft Autopatch, Tanium, ServiceNow: Strengths and Limitations
Comparing enterprise patch management solutions reveals distinct differences among Microsoft Autopatch, Tanium, ServiceNow, and Ivanti Neurons.
Microsoft Autopatch uses ring deployment but is limited to Windows and Microsoft 365 environments. Ivanti Neurons supports a wider range, including Windows, macOS, Linux, and third-party applications, ideal for diverse infrastructures.
Tanium excels in endpoint visibility and reporting but requires significant resources, suiting larger enterprises. ServiceNow shines in workflow automation and IT service integration but often needs customization for patching.
Ivanti Neurons stands out with dynamic risk assessments, phased ring deployments, and automated workflows in one platform, addressing visibility gaps, complexity, and prioritization challenges with real-time dashboards.

Turning Patch Management into a Strategic Asset
Patching alone isn’t enough to eliminate vulnerabilities. Gartner emphasizes integrating endpoint protection, multifactor authentication, and network segmentation to bolster security beyond patching.
Pairing ring deployment with zero-trust controls enables IT teams to minimize exposure windows and manage risks effectively.
Ivanti’s ring deployment integrates real-time risk assessments, automated remediation, and threat management, aligning patch management with business resilience. Built into Ivanti Neurons, it provides scalable, real-time risk visibility.
Conclusion: Combining ring deployment with prioritization tools and compensating controls transforms patch management into a proactive, strategic advantage.
 Vast Data Targets $25B Valuation in Latest Funding Round
Vast Data, a provider of AI-optimized data storage solutions, is seeking to raise funds at a significantly higher valuation.Earlier this year, the nine-year-old firm aimed for a $25 billion valuation,
Vast Data Targets $25B Valuation in Latest Funding Round
Vast Data, a provider of AI-optimized data storage solutions, is seeking to raise funds at a significantly higher valuation.Earlier this year, the nine-year-old firm aimed for a $25 billion valuation,
 Kawtco L815 AI Voice Recorder: Unboxing and Comprehensive User Guide
In today’s fast-moving world, a dependable voice recorder is essential. The Kawtco L815 AI Voice Recorder delivers cutting-edge AI features, making it ideal for diverse needs. From capturing phone cal
Kawtco L815 AI Voice Recorder: Unboxing and Comprehensive User Guide
In today’s fast-moving world, a dependable voice recorder is essential. The Kawtco L815 AI Voice Recorder delivers cutting-edge AI features, making it ideal for diverse needs. From capturing phone cal
 OpenAI Commits to Fixes After ChatGPT's Overly Agreeable Responses
OpenAI plans to revise its AI model update process for ChatGPT after an update caused excessively sycophantic responses, prompting widespread user feedback.Last weekend, following an update to GPT-4o,
OpenAI Commits to Fixes After ChatGPT's Overly Agreeable Responses
OpenAI plans to revise its AI model update process for ChatGPT after an update caused excessively sycophantic responses, prompting widespread user feedback.Last weekend, following an update to GPT-4o,