PydanticAI Graphs Transform AI Agent Workflows
PydanticAI has recently rolled out a game-changing feature known as PydanticAI Graphs, which promises to transform the way AI agents manage and execute workflows. This new tool offers developers a way to model, control, and visualize complex AI interactions with an unprecedented level of clarity and efficiency. In this article, we'll dive into the world of PydanticAI Graphs, an asynchronous graph and state machine library, exploring its key features, benefits, and its potential to revolutionize AI development.
Key Points
- PydanticAI introduces graph support for modeling AI agent workflows.
- These graphs function as asynchronous state machines, defined using type hints.
- The library targets intermediate to advanced developers, providing sophisticated control options.
- Core components include GraphRunContext, End, Nodes, and Graph.
- It's designed to enhance decision-making processes in AI applications.
- These core components serve as the fundamental building blocks of PydanticAI Graphs.
Understanding PydanticAI Graphs
What are PydanticAI Graphs?
PydanticAI Graphs is an asynchronous graph and state machine library built specifically for Python, enabling developers to define nodes and edges with type hints. This structured approach allows for the design of intricate AI agent interactions.
This library empowers developers to model, execute, control, and visualize complex workflows with remarkable clarity. By using PydanticAI Graphs, you can create more robust, understandable, and maintainable AI applications, setting a new standard in AI agent design. The combination of graphs and finite state machines offers a powerful abstraction for managing complex workflows.
Target Audience
PydanticAI Graphs are tailored for intermediate to advanced developers, rather than beginners. This tool requires a solid understanding of Python and graph data structures.
Given its advanced nature, the library leverages Python generics and type hints to streamline the development process. For developers experienced with graph data structures, PydanticAI Graphs provides unmatched power and flexibility.
Installation
Getting started with PydanticAI Graphs is straightforward. You can install it using pip:
pip install pydantic-graph
It's recommended to have PydanticAI installed as well, though it's an optional dependency.
Key Components of PydanticAI Graphs
PydanticAI Graphs are built around four core components crucial for understanding and utilizing the library effectively:
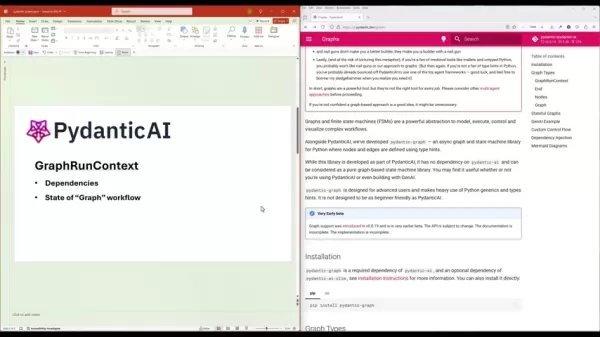
- GraphRunContext: Similar to the RunContext in PydanticAI, this component manages the state of the graph and its dependencies. It's like the baton in a relay race, passing vital information between nodes to ensure smooth execution.
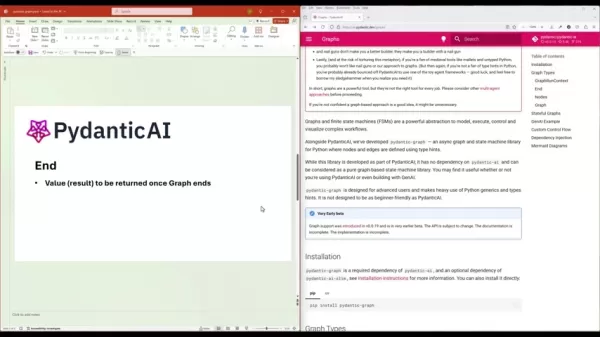
- End: This signifies the end of graph execution, marking when a node has returned its final value. It's the finish line of the race, signaling the workflow's completion, which is especially helpful in managing complex workflows with many actions.
- Nodes: These are the core units of the graph, executing process logic through the run method.
- Graph: Acts as the execution engine, composed of nodes. It's the master blueprint that orchestrates the entire workflow, akin to a pipeline that triggers tasks.
Advanced Topics in PydanticAI Graphs
Graph Data Structures and Their Importance
In computer science, graphs are abstract data types that represent connections between entities. They consist of vertices (or nodes) and edges, which can be directed or undirected.
Graphs have numerous applications, from modeling transportation and utility networks to social networks and molecular structures. They're essential for representing complex relationships and systems.
State Machines Explained
A state machine is a computational model that can be in one of a finite number of states at any time. It changes states in response to inputs, with these changes known as transitions.

State machines are crucial for modeling complex systems, designing robot controllers, analyzing computer languages, and developing video games. They can be visualized as directed graphs, where nodes represent states and edges represent transitions.
How to Use PydanticAI Graph
Coding a Simple Graph
Let's set up a simple graph with three nodes:
- Node A as the starting node.
- Node B as the decision-making node.
- Node C as the end of the process.
Each node shares a base class type, which is crucial. First, import the necessary components:
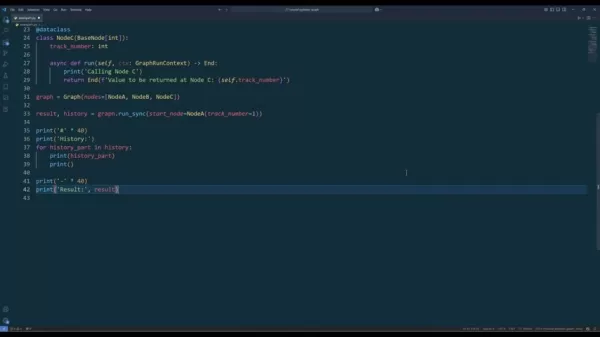
from dataclasses import dataclass
from pydantic_graph import GraphRunContext, BaseNode, Graph, End
@dataclass
class NodeA(BaseNode[int]):
track_number: int
@dataclass
class NodeB(BaseNode[int]):
track_number: int
@dataclass
class NodeC(BaseNode[int]):
track_number: int
Coding async Run Methods
Now, let's code the async run methods for these nodes:
@dataclass
class NodeA(BaseNode[int]):
track_number: int
async def run(self, ctx: GraphRunContext) -> BaseNode:
print(f'Calling Node A')
return NodeB(self.track_number)
@dataclass
class NodeB(BaseNode[int]):
track_number: int
async def run(self, ctx: GraphRunContext) -> BaseNode | End:
print(f'Calling Node B')
if self.track_number == 1:
return End(f'Stop at Node B with value --> {self.track_number}')
else:
return NodeC(self.track_number)
@dataclass
class NodeC(BaseNode[int]):
track_number: int
async def run(self, ctx: GraphRunContext) -> End:
print(f'Calling Node C')
return End(f'Value to be returned at Node C: {self.track_number}')
Node A passes the track to Node B, which then decides whether to stop the execution or proceed to Node C.
Run
Finally, initialize the graph and run it:
graph = Graph(nodes=[NodeA, NodeB, NodeC])
result, history = graph.run_sync(start_node=NodeA(track_number=1))
print('*' * 40)
print('History:')
for history_part in history:
print(history_part)
print('*' * 40)
print(f'Result: {result}')
This code will call Node A, then stop the execution at Node B with a track value of 1.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using PydanticAI Graphs
Pros
- Enhanced workflow modeling and visualization.
- Asynchronous operation for high performance.
- Type hints for robust code.
- Independent usage possible.
Cons
- Steep learning curve for beginners.
- Early beta status may include bugs and incomplete documentation.
FAQ
What is PydanticAI?
PydanticAI is an AI framework designed to streamline the development, deployment, and management of AI applications. It integrates asynchronous programming, data validation, and workflow management into a cohesive system.
What is the primary benefit of using PydanticAI Graphs?
PydanticAI Graphs enable developers to create complex AI agent workflows with greater clarity and control. The graph structure allows for easier modeling and visualization of these workflows, enhancing maintainability and performance.
Does PydanticAI Graphs depend on other PydanticAI components?
While developed as part of PydanticAI, PydanticAI Graphs does not have dependencies on other components and can be used independently for graph-based state machine applications. This flexibility makes it suitable for a wide range of projects.
Related Questions
What are the alternatives to PydanticAI?
Alternatives for building AI agents and workflows include:
- Langchain: A framework for creating applications using Large Language Models (LLMs).
- AutoGen: Developed by Microsoft, it helps developers build conversational AI by orchestrating multiple agents that can converse to solve tasks.
- Haystack: An open-source framework from deepset that enables developers to build intelligent search applications over large document collections.
Related article
 Easily Create Stunning Comics with AI-Powered Comic Factory
Comic Factory AI represents a quantum leap in digital storytelling, transforming how visual narratives are crafted. This groundbreaking platform leverages artificial intelligence to instantly convert text descriptions into professional-grade comic ar
Easily Create Stunning Comics with AI-Powered Comic Factory
Comic Factory AI represents a quantum leap in digital storytelling, transforming how visual narratives are crafted. This groundbreaking platform leverages artificial intelligence to instantly convert text descriptions into professional-grade comic ar
 Capital One Develops AI Agent to Boost Automotive Sales Efficiency
Innovation in Agentic System Design: Cross-Industry InspirationWhen developing intelligent agent systems, creative inspiration can emerge from unexpected sources - even organizational structures themselves. At VB Transform, Capital One revealed how i
Capital One Develops AI Agent to Boost Automotive Sales Efficiency
Innovation in Agentic System Design: Cross-Industry InspirationWhen developing intelligent agent systems, creative inspiration can emerge from unexpected sources - even organizational structures themselves. At VB Transform, Capital One revealed how i
 Boost Business Growth with Creator Pro AI & ChatGPT Optimization
In today's competitive business landscape, artificial intelligence solutions have transitioned from optional upgrades to essential operational assets. Picture having access to a comprehensive AI toolkit, where each specialized application addresses s
Comments (14)
0/200
Boost Business Growth with Creator Pro AI & ChatGPT Optimization
In today's competitive business landscape, artificial intelligence solutions have transitioned from optional upgrades to essential operational assets. Picture having access to a comprehensive AI toolkit, where each specialized application addresses s
Comments (14)
0/200
![JustinMitchell]() JustinMitchell
JustinMitchell
 October 15, 2025 at 10:30:34 AM EDT
October 15, 2025 at 10:30:34 AM EDT
This looks like a game-changer for workflow management! The ability to visualize AI interactions could make debugging so much easier. 🚀 I'm curious how this compares to LangGraph in real-world applications though - anyone tried both yet?


 0
0
![ThomasYoung]() ThomasYoung
ThomasYoung
 August 8, 2025 at 1:01:00 PM EDT
August 8, 2025 at 1:01:00 PM EDT
PydanticAI Graphs sound like a game-changer for AI workflows! The ability to visualize complex interactions is super cool, but I wonder how steep the learning curve is for newbies. 🤔 Anyone tried it yet?


 0
0
![JoseDavis]() JoseDavis
JoseDavis
 July 31, 2025 at 7:35:39 AM EDT
July 31, 2025 at 7:35:39 AM EDT
Cette fonctionnalité de PydanticAI Graphs semble révolutionnaire, mais est-ce vraiment accessible aux développeurs moins expérimentés ou juste un jouet pour les pros ? 🤔


 0
0
![OliverAnderson]() OliverAnderson
OliverAnderson
 July 27, 2025 at 9:20:03 PM EDT
July 27, 2025 at 9:20:03 PM EDT
This PydanticAI Graphs thing sounds like a total game-changer for AI workflows! 😎 I'm curious, how easy is it to integrate with existing Python projects?


 0
0
![BruceSmith]() BruceSmith
BruceSmith
 May 10, 2025 at 11:59:24 AM EDT
May 10, 2025 at 11:59:24 AM EDT
PydanticAI Graphs es un cambio de juego total para gestionar flujos de trabajo de IA. ¡Es como tener un mapa para navegar por interacciones de IA complejas! La visualización es súper clara, pero a veces puede ser un poco abrumadora. Aún así, es imprescindible para cualquier desarrollador que trabaje con agentes de IA. ¡Altamente recomendado! 🚀


 0
0
![RogerPerez]() RogerPerez
RogerPerez
 May 10, 2025 at 8:31:00 AM EDT
May 10, 2025 at 8:31:00 AM EDT
PydanticAI Graphs는 AI 워크플로우 관리에 혁신을 가져왔어요! 직관적이고 시각화도 완벽해요. 유일한 단점은 학습 곡선이 가파르다는 점이지만, 한 번 이해하면 부드럽게 진행됩니다. AI 개발에 관심이 있다면 강력 추천해요! 🚀


 0
0
PydanticAI has recently rolled out a game-changing feature known as PydanticAI Graphs, which promises to transform the way AI agents manage and execute workflows. This new tool offers developers a way to model, control, and visualize complex AI interactions with an unprecedented level of clarity and efficiency. In this article, we'll dive into the world of PydanticAI Graphs, an asynchronous graph and state machine library, exploring its key features, benefits, and its potential to revolutionize AI development.
Key Points
- PydanticAI introduces graph support for modeling AI agent workflows.
- These graphs function as asynchronous state machines, defined using type hints.
- The library targets intermediate to advanced developers, providing sophisticated control options.
- Core components include GraphRunContext, End, Nodes, and Graph.
- It's designed to enhance decision-making processes in AI applications.
- These core components serve as the fundamental building blocks of PydanticAI Graphs.
Understanding PydanticAI Graphs
What are PydanticAI Graphs?
PydanticAI Graphs is an asynchronous graph and state machine library built specifically for Python, enabling developers to define nodes and edges with type hints. This structured approach allows for the design of intricate AI agent interactions.

This library empowers developers to model, execute, control, and visualize complex workflows with remarkable clarity. By using PydanticAI Graphs, you can create more robust, understandable, and maintainable AI applications, setting a new standard in AI agent design. The combination of graphs and finite state machines offers a powerful abstraction for managing complex workflows.
Target Audience
PydanticAI Graphs are tailored for intermediate to advanced developers, rather than beginners. This tool requires a solid understanding of Python and graph data structures.

Given its advanced nature, the library leverages Python generics and type hints to streamline the development process. For developers experienced with graph data structures, PydanticAI Graphs provides unmatched power and flexibility.
Installation
Getting started with PydanticAI Graphs is straightforward. You can install it using pip:
pip install pydantic-graph
It's recommended to have PydanticAI installed as well, though it's an optional dependency.
Key Components of PydanticAI Graphs
PydanticAI Graphs are built around four core components crucial for understanding and utilizing the library effectively:
- GraphRunContext: Similar to the RunContext in PydanticAI, this component manages the state of the graph and its dependencies. It's like the baton in a relay race, passing vital information between nodes to ensure smooth execution.
- End: This signifies the end of graph execution, marking when a node has returned its final value. It's the finish line of the race, signaling the workflow's completion, which is especially helpful in managing complex workflows with many actions.
- Nodes: These are the core units of the graph, executing process logic through the run method.
- Graph: Acts as the execution engine, composed of nodes. It's the master blueprint that orchestrates the entire workflow, akin to a pipeline that triggers tasks.

Advanced Topics in PydanticAI Graphs
Graph Data Structures and Their Importance
In computer science, graphs are abstract data types that represent connections between entities. They consist of vertices (or nodes) and edges, which can be directed or undirected.

Graphs have numerous applications, from modeling transportation and utility networks to social networks and molecular structures. They're essential for representing complex relationships and systems.
State Machines Explained
A state machine is a computational model that can be in one of a finite number of states at any time. It changes states in response to inputs, with these changes known as transitions.

State machines are crucial for modeling complex systems, designing robot controllers, analyzing computer languages, and developing video games. They can be visualized as directed graphs, where nodes represent states and edges represent transitions.
How to Use PydanticAI Graph
Coding a Simple Graph
Let's set up a simple graph with three nodes:
- Node A as the starting node.
- Node B as the decision-making node.
- Node C as the end of the process.
Each node shares a base class type, which is crucial. First, import the necessary components:

from dataclasses import dataclass
from pydantic_graph import GraphRunContext, BaseNode, Graph, End
@dataclass
class NodeA(BaseNode[int]):
track_number: int
@dataclass
class NodeB(BaseNode[int]):
track_number: int
@dataclass
class NodeC(BaseNode[int]):
track_number: int
Coding async Run Methods
Now, let's code the async run methods for these nodes:
@dataclass
class NodeA(BaseNode[int]):
track_number: int
async def run(self, ctx: GraphRunContext) -> BaseNode:
print(f'Calling Node A')
return NodeB(self.track_number)
@dataclass
class NodeB(BaseNode[int]):
track_number: int
async def run(self, ctx: GraphRunContext) -> BaseNode | End:
print(f'Calling Node B')
if self.track_number == 1:
return End(f'Stop at Node B with value --> {self.track_number}')
else:
return NodeC(self.track_number)
@dataclass
class NodeC(BaseNode[int]):
track_number: int
async def run(self, ctx: GraphRunContext) -> End:
print(f'Calling Node C')
return End(f'Value to be returned at Node C: {self.track_number}')
Node A passes the track to Node B, which then decides whether to stop the execution or proceed to Node C.
Run
Finally, initialize the graph and run it:
graph = Graph(nodes=[NodeA, NodeB, NodeC])
result, history = graph.run_sync(start_node=NodeA(track_number=1))
print('*' * 40)
print('History:')
for history_part in history:
print(history_part)
print('*' * 40)
print(f'Result: {result}')This code will call Node A, then stop the execution at Node B with a track value of 1.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using PydanticAI Graphs
Pros
- Enhanced workflow modeling and visualization.
- Asynchronous operation for high performance.
- Type hints for robust code.
- Independent usage possible.
Cons
- Steep learning curve for beginners.
- Early beta status may include bugs and incomplete documentation.
FAQ
What is PydanticAI?
PydanticAI is an AI framework designed to streamline the development, deployment, and management of AI applications. It integrates asynchronous programming, data validation, and workflow management into a cohesive system.
What is the primary benefit of using PydanticAI Graphs?
PydanticAI Graphs enable developers to create complex AI agent workflows with greater clarity and control. The graph structure allows for easier modeling and visualization of these workflows, enhancing maintainability and performance.
Does PydanticAI Graphs depend on other PydanticAI components?
While developed as part of PydanticAI, PydanticAI Graphs does not have dependencies on other components and can be used independently for graph-based state machine applications. This flexibility makes it suitable for a wide range of projects.
Related Questions
What are the alternatives to PydanticAI?
Alternatives for building AI agents and workflows include:
- Langchain: A framework for creating applications using Large Language Models (LLMs).
- AutoGen: Developed by Microsoft, it helps developers build conversational AI by orchestrating multiple agents that can converse to solve tasks.
- Haystack: An open-source framework from deepset that enables developers to build intelligent search applications over large document collections.
 Easily Create Stunning Comics with AI-Powered Comic Factory
Comic Factory AI represents a quantum leap in digital storytelling, transforming how visual narratives are crafted. This groundbreaking platform leverages artificial intelligence to instantly convert text descriptions into professional-grade comic ar
Easily Create Stunning Comics with AI-Powered Comic Factory
Comic Factory AI represents a quantum leap in digital storytelling, transforming how visual narratives are crafted. This groundbreaking platform leverages artificial intelligence to instantly convert text descriptions into professional-grade comic ar
 Capital One Develops AI Agent to Boost Automotive Sales Efficiency
Innovation in Agentic System Design: Cross-Industry InspirationWhen developing intelligent agent systems, creative inspiration can emerge from unexpected sources - even organizational structures themselves. At VB Transform, Capital One revealed how i
Capital One Develops AI Agent to Boost Automotive Sales Efficiency
Innovation in Agentic System Design: Cross-Industry InspirationWhen developing intelligent agent systems, creative inspiration can emerge from unexpected sources - even organizational structures themselves. At VB Transform, Capital One revealed how i
 Boost Business Growth with Creator Pro AI & ChatGPT Optimization
In today's competitive business landscape, artificial intelligence solutions have transitioned from optional upgrades to essential operational assets. Picture having access to a comprehensive AI toolkit, where each specialized application addresses s
Boost Business Growth with Creator Pro AI & ChatGPT Optimization
In today's competitive business landscape, artificial intelligence solutions have transitioned from optional upgrades to essential operational assets. Picture having access to a comprehensive AI toolkit, where each specialized application addresses s
 October 15, 2025 at 10:30:34 AM EDT
October 15, 2025 at 10:30:34 AM EDT
This looks like a game-changer for workflow management! The ability to visualize AI interactions could make debugging so much easier. 🚀 I'm curious how this compares to LangGraph in real-world applications though - anyone tried both yet?


 0
0
 August 8, 2025 at 1:01:00 PM EDT
August 8, 2025 at 1:01:00 PM EDT
PydanticAI Graphs sound like a game-changer for AI workflows! The ability to visualize complex interactions is super cool, but I wonder how steep the learning curve is for newbies. 🤔 Anyone tried it yet?


 0
0
 July 31, 2025 at 7:35:39 AM EDT
July 31, 2025 at 7:35:39 AM EDT
Cette fonctionnalité de PydanticAI Graphs semble révolutionnaire, mais est-ce vraiment accessible aux développeurs moins expérimentés ou juste un jouet pour les pros ? 🤔


 0
0
 July 27, 2025 at 9:20:03 PM EDT
July 27, 2025 at 9:20:03 PM EDT
This PydanticAI Graphs thing sounds like a total game-changer for AI workflows! 😎 I'm curious, how easy is it to integrate with existing Python projects?


 0
0
 May 10, 2025 at 11:59:24 AM EDT
May 10, 2025 at 11:59:24 AM EDT
PydanticAI Graphs es un cambio de juego total para gestionar flujos de trabajo de IA. ¡Es como tener un mapa para navegar por interacciones de IA complejas! La visualización es súper clara, pero a veces puede ser un poco abrumadora. Aún así, es imprescindible para cualquier desarrollador que trabaje con agentes de IA. ¡Altamente recomendado! 🚀


 0
0
 May 10, 2025 at 8:31:00 AM EDT
May 10, 2025 at 8:31:00 AM EDT
PydanticAI Graphs는 AI 워크플로우 관리에 혁신을 가져왔어요! 직관적이고 시각화도 완벽해요. 유일한 단점은 학습 곡선이 가파르다는 점이지만, 한 번 이해하면 부드럽게 진행됩니다. AI 개발에 관심이 있다면 강력 추천해요! 🚀


 0
0