Beginner's Guide to Understanding Domain Name Basics

 April 25, 2025
April 25, 2025

 BillyGarcía
BillyGarcía
 0
0
Embarking on the journey of starting an online business or setting up a personal website? The first thing you'll need to get your head around is the concept of domain names. But what exactly is a domain name, and how does it function? This guide will demystify the essentials, helping you confidently navigate the realm of domain names. Whether you're kicking off a new site or simply curious, we've got all the information you need to get started.
Understanding Domain Names
What is a Domain Name?
A domain name is essentially the internet's version of your home address, but instead of directing someone to your physical location, it leads them to your website. Imagine trying to remember a string of numbers (that's your IP address) every time you want to visit a site. Sounds tedious, right? That's where domain names come in handy. They're user-friendly labels like 'businessnamegenerator.com' that make it easy for people to find your site.
Think of the internet as a bustling Spanish town. If you run a business there, your customers need an address to locate you. A domain name serves the same purpose for your website. Instead of '4 Main Street,' you might have 'yourbusiness.com.' It's simple, memorable, and essential for your online presence.
A typical domain name consists of two parts:
- The Name: This is your unique identifier (e.g., 'businessnamegenerator'). It should be memorable, relevant to your business, and easy to spell.
- The Extension: This is the suffix at the end of the name (e.g., '.com,' '.org,' '.net'). Different extensions can signify the purpose or type of your website. For instance, '.com' is commonly used for commercial sites, while '.org' is popular among non-profits.
Why are domain names so crucial?
- Branding: A good domain name reinforces your brand identity and helps customers remember your site.
- Credibility: A professional domain name adds a layer of trust to your online presence.
- SEO: Using relevant keywords in your domain name can boost your site's search engine ranking.
- Marketing: A memorable domain name is easier to share and market to potential customers.
Choosing the right domain name is more than just picking an address; it's a cornerstone of your online brand.
How Domain Names Work: From Domain to Website
When you enter a domain name into your browser, you're not directly accessing the website's actual address, which is an IP address. IP addresses are numerical labels assigned to devices connected to the internet. Domain names serve as a user-friendly mask over these numbers, making it easier for us to remember and use them.

Computers and modems don't communicate with letters; they use numbers. That's why IP addresses are essential. The domain name is like a convenient alias, allowing people to avoid memorizing long strings of numbers and instead find a website through an intuitive name.
The magic behind translating domain names to IP addresses is the Domain Name System (DNS). Think of DNS as the internet's phonebook. When you type a domain name into your browser, your computer sends a request to a DNS server. The DNS server looks up the corresponding IP address and sends it back to your computer, which then uses it to connect to the web server hosting your website. All of this happens in milliseconds, making the process seamless for the user.
In essence, DNS acts as a translator, converting the domain name you enter into the IP address your computer needs to locate the website. Without DNS, you'd have to remember the IP address of every site you visit!
Domain names simplify the internet by providing easy-to-remember addresses, while DNS ensures that computers can efficiently find the corresponding web servers. Here's a simple breakdown:
Component Function Analogy Domain Name User-friendly website address Business Name IP Address Numerical address computers use Street Address DNS Translates domain names to IP addresses Phonebook Web Server Hosts the website's content Physical Store Location Web Browser Used to enter domain names and view website content Customer
Understanding how domain names work gives you a better grasp of the fundamental processes behind web navigation and a deeper appreciation for the complex infrastructure that makes the internet so accessible and user-friendly.
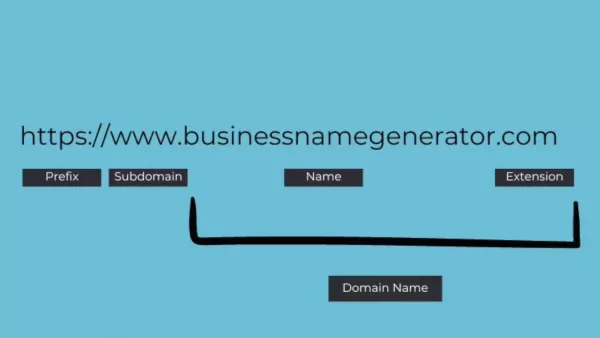
Domain Name vs. URL: What's the Difference?
It's easy to confuse domain names with URLs, but they're not the same thing. A domain name is the core identifier for your website (e.g., 'example.com'), while a URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is the full web address that specifies the exact location of a resource on the internet.
Think of a URL as the complete address of a specific building, while the domain name is just the name of the street it's on. Here's how they break down:
- Domain Name: The core identifier for your website.
- URL: Contains additional information such as:
- Protocol: Indicates how your browser should communicate with the web server (e.g., 'https://'). 'HTTPS' ensures a secure connection, encrypting data transmitted between your browser and the website.
- Subdomain: A prefix to the domain name (e.g., 'www'). While 'WWW' used to be standard, it's now often optional.
- Path: Specifies the exact location of a specific page or resource on the server (e.g., '/blog/how-to-choose-a-domain-name'). The path directs the server to the specific file or content you want to access.
- Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN): The complete domain name, including the hostname (e.g., 'www.example.com'). The FQDN helps the DNS accurately locate the web server.
So, while a domain name is a crucial part of a URL, it's not the whole story. A URL provides all the necessary information for your browser to find and display a specific web page or resource.
For example:
- Domain Name: businessnamegenerator.com
- Fully Qualified Domain Name: www.businessnamegenerator.com
- URL: https://www.businessnamegenerator.com/what-is-a-domain-name/
Understanding the distinction between domain names and URLs helps you navigate the web with greater clarity and appreciate the intricacies of web addressing.
Choosing the Right Domain Name
Tips for Selecting a Great Domain Name
Choosing the perfect domain name is vital for building a strong online presence. A well-chosen domain can boost your brand, improve your SEO, and make it easier for customers to find you. Here are some tips to help you make the right choice:
- Keep it Short and Memorable: Shorter domain names are easier to remember and type. Aim for a name that's concise and catchy to stick in people's minds.
- Use Relevant Keywords: Incorporate keywords related to your business or website into your domain name. This can enhance your search engine ranking and help potential customers understand what your site is about.
- Choose the Right Extension: '.com' is the most common and widely recognized extension, but consider others like '.net,' '.org,' or industry-specific extensions if they better suit your needs.
- Make it Easy to Spell and Pronounce: Avoid unusual spellings or words that are hard to pronounce. A domain name that's easy to say and spell reduces the chances of typos and makes it easier for people to share your website.
- Check for Availability: Before settling on a domain name, ensure it's available. Use a domain name registrar to check if the name is already registered.
- Consider Your Brand: Your domain name should reflect your brand identity and values. Choose a name that aligns with your business name, logo, and overall brand messaging.
- Avoid Hyphens and Numbers: Hyphens and numbers can make your domain name harder to remember and type. It's generally best to avoid them unless they're essential to your brand.
- Protect Your Brand: Register variations of your domain name to prevent competitors from using similar names. This includes registering different extensions and common misspellings of your domain name.
By following these tips, you can select a domain name that sets your website up for success. A strong domain name is a valuable asset that can enhance your online visibility, brand recognition, and overall business growth.
Using Business Name Generator to Find a Domain Name
Steps to Generate and Select a Domain Name
Business Name Generator isn't just for finding business names; it can also help you discover available domain names related to your business idea. Here's how to use it:
- Enter Keywords: Start by entering keywords related to your business or website into the Business Name Generator search bar.
- Generate Names: Click the 'Generate' button to produce a list of potential business names and domain name suggestions.
- Filter Results: Use the filters to narrow down the results based on your preferences, such as length, style, and industry.
- Check Availability: Once you find a name you like, check its domain name availability. Business Name Generator often provides domain availability checks directly within the search results.
- Refine Your Search: If your initial search doesn't yield the perfect result, try different keywords or filters to refine your search.
- Register Your Domain: Once you find an available domain name that aligns with your brand, register it through a reputable domain name registrar.
Business Name Generator simplifies the domain name search process, helping you brainstorm ideas and quickly assess availability. It's a valuable tool for anyone starting an online business or launching a new website.
Pros and Cons of Using Business Name Generator
Pros:
- Provides a wide range of name suggestions.
- Helps with brainstorming creative business and domain names.
- Often includes domain availability checks.
- User-friendly interface for easy navigation.
- Saves time compared to manual brainstorming.
Cons:
- Some suggestions may not be relevant to your specific business.
- The best names may already be taken.
- Can generate generic names that lack originality.
- Domain availability checks may not always be accurate.
- Relies on keyword input, which may limit creativity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What if my desired .com domain name is already taken?
If your first choice for a .com domain is unavailable, don't worry. You have several options:
- Consider Alternative Extensions: Explore other domain extensions like .net, .org, .info, .biz, or country-specific extensions (e.g., .ca for Canada, .uk for the United Kingdom). Some of these extensions may be available and still suitable for your website.
- Get Creative with the Name: Try adding a word or phrase to your desired domain name to make it unique. For example, if 'example.com' is taken, try 'getexample.com' or 'exampleonline.com.'
- Negotiate with the Owner: If you're set on a specific domain name, you can try to contact the current owner and offer to buy it. Domain name brokers can help facilitate this process.
- Consider a Different Name: If all else fails, it might be best to choose a completely different domain name that's available and aligns with your brand. Remember to prioritize brand relevance and memorability when considering alternatives.
How much does a domain name typically cost?
The cost of a domain name can vary depending on several factors, including:
- Extension: .com domains are often priced higher than less common extensions.
- Registrar: Different domain name registrars may offer different prices.
- Registration Period: Most registrars offer discounts for longer registration periods (e.g., multiple years).
- Domain Privacy: Adding domain privacy protection can increase the cost.
- Premium Domains: Some domain names are considered 'premium' and can command much higher prices.
Typically, you can expect to pay anywhere from $10 to $20 per year for a standard .com domain name. However, premium domains can cost hundreds or even thousands of dollars. It's important to compare prices from different registrars and consider the additional services offered.
Do I need web hosting to have a domain name?
Yes, you typically need web hosting to make your website accessible online. Here's why:
- Domain Name: Your domain name is your website's address. It tells people how to find you.
- Web Hosting: Web hosting is where your website's files are stored. It's the physical location of your website on the internet.
Think of your domain name as your street address and web hosting as the actual building on that street. Without a building (web hosting), there's nowhere for people to visit even if they have your address (domain name). When someone types your domain name into their browser, the DNS directs them to the web server hosting your website's files. If you don't have web hosting, there's no server to respond to the request, and your website won't be accessible.
Related Questions
How do I transfer a domain name from one registrar to another?
Transferring a domain name involves moving the registration of your domain from one domain registrar to another. Here's a general outline of the process:
- Unlock Your Domain: Log in to your current domain registrar and unlock your domain name. This prevents unauthorized transfers.
- Obtain an Authorization Code (EPP Code): Request an authorization code (also known as an EPP code or transfer code) from your current registrar. This code is required to initiate the transfer.
- Initiate the Transfer with the New Registrar: Go to the website of your new domain registrar and initiate the domain transfer process. You'll need to provide the domain name and authorization code.
- Approve the Transfer: Your current registrar will send you an email asking you to approve the transfer. Follow the instructions in the email to confirm the transfer.
- Wait for the Transfer to Complete: The transfer process typically takes 5-7 days to complete. During this time, your website should remain accessible.
It's important to note that you may need to wait at least 60 days after registering or transferring a domain name before you can transfer it again. Also, ensure that your domain name is not expired or close to expiring before initiating the transfer.
Related article
 Pickaxe: Monetize AI Tools Without Coding in 2025
Exploring Pickaxe: The Future of No-Code AI Development?The world of AI tool development is constantly evolving, and Pickaxe is making a significant impact by allowing users to create, deploy, and monetize AI-powered tools without any coding knowledge. Is this the future we're heading towards for no
Pickaxe: Monetize AI Tools Without Coding in 2025
Exploring Pickaxe: The Future of No-Code AI Development?The world of AI tool development is constantly evolving, and Pickaxe is making a significant impact by allowing users to create, deploy, and monetize AI-powered tools without any coding knowledge. Is this the future we're heading towards for no
 Future-Proof Your UX Career: Essential Skills for Success in 2025
In the ever-changing world of UX and product design, it's clear that the field isn't dying—it's transforming. To stay ahead, designers must focus on key growth areas to remain competitive. As AI and automation reshape how we design, it's essential to evolve from just being creators to becoming curat
Future-Proof Your UX Career: Essential Skills for Success in 2025
In the ever-changing world of UX and product design, it's clear that the field isn't dying—it's transforming. To stay ahead, designers must focus on key growth areas to remain competitive. As AI and automation reshape how we design, it's essential to evolve from just being creators to becoming curat
 How AI will transform cybersecurity in 2025 - and supercharge cybercrime
The cybersecurity landscape in 2024 was rocked by severe ransomware attacks, AI-driven social engineering, and state-sponsored cyber operations that racked up billions in damages. As we step into 2025, the mix of AI advancements, geopolitical tensions, and increasingly complex attack surfaces is set
Comments (0)
0/200
How AI will transform cybersecurity in 2025 - and supercharge cybercrime
The cybersecurity landscape in 2024 was rocked by severe ransomware attacks, AI-driven social engineering, and state-sponsored cyber operations that racked up billions in damages. As we step into 2025, the mix of AI advancements, geopolitical tensions, and increasingly complex attack surfaces is set
Comments (0)
0/200

 April 25, 2025
April 25, 2025

 BillyGarcía
BillyGarcía

 0
0
Embarking on the journey of starting an online business or setting up a personal website? The first thing you'll need to get your head around is the concept of domain names. But what exactly is a domain name, and how does it function? This guide will demystify the essentials, helping you confidently navigate the realm of domain names. Whether you're kicking off a new site or simply curious, we've got all the information you need to get started.
Understanding Domain Names
What is a Domain Name?
A domain name is essentially the internet's version of your home address, but instead of directing someone to your physical location, it leads them to your website. Imagine trying to remember a string of numbers (that's your IP address) every time you want to visit a site. Sounds tedious, right? That's where domain names come in handy. They're user-friendly labels like 'businessnamegenerator.com' that make it easy for people to find your site.

Think of the internet as a bustling Spanish town. If you run a business there, your customers need an address to locate you. A domain name serves the same purpose for your website. Instead of '4 Main Street,' you might have 'yourbusiness.com.' It's simple, memorable, and essential for your online presence.
A typical domain name consists of two parts:
- The Name: This is your unique identifier (e.g., 'businessnamegenerator'). It should be memorable, relevant to your business, and easy to spell.
- The Extension: This is the suffix at the end of the name (e.g., '.com,' '.org,' '.net'). Different extensions can signify the purpose or type of your website. For instance, '.com' is commonly used for commercial sites, while '.org' is popular among non-profits.
Why are domain names so crucial?
- Branding: A good domain name reinforces your brand identity and helps customers remember your site.
- Credibility: A professional domain name adds a layer of trust to your online presence.
- SEO: Using relevant keywords in your domain name can boost your site's search engine ranking.
- Marketing: A memorable domain name is easier to share and market to potential customers.
Choosing the right domain name is more than just picking an address; it's a cornerstone of your online brand.
How Domain Names Work: From Domain to Website
When you enter a domain name into your browser, you're not directly accessing the website's actual address, which is an IP address. IP addresses are numerical labels assigned to devices connected to the internet. Domain names serve as a user-friendly mask over these numbers, making it easier for us to remember and use them.

Computers and modems don't communicate with letters; they use numbers. That's why IP addresses are essential. The domain name is like a convenient alias, allowing people to avoid memorizing long strings of numbers and instead find a website through an intuitive name.
The magic behind translating domain names to IP addresses is the Domain Name System (DNS). Think of DNS as the internet's phonebook. When you type a domain name into your browser, your computer sends a request to a DNS server. The DNS server looks up the corresponding IP address and sends it back to your computer, which then uses it to connect to the web server hosting your website. All of this happens in milliseconds, making the process seamless for the user.
In essence, DNS acts as a translator, converting the domain name you enter into the IP address your computer needs to locate the website. Without DNS, you'd have to remember the IP address of every site you visit!
Domain names simplify the internet by providing easy-to-remember addresses, while DNS ensures that computers can efficiently find the corresponding web servers. Here's a simple breakdown:
| Component | Function | Analogy |
|---|---|---|
| Domain Name | User-friendly website address | Business Name |
| IP Address | Numerical address computers use | Street Address |
| DNS | Translates domain names to IP addresses | Phonebook |
| Web Server | Hosts the website's content | Physical Store Location |
| Web Browser | Used to enter domain names and view website content | Customer |
Understanding how domain names work gives you a better grasp of the fundamental processes behind web navigation and a deeper appreciation for the complex infrastructure that makes the internet so accessible and user-friendly.
Domain Name vs. URL: What's the Difference?
It's easy to confuse domain names with URLs, but they're not the same thing. A domain name is the core identifier for your website (e.g., 'example.com'), while a URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is the full web address that specifies the exact location of a resource on the internet.
Think of a URL as the complete address of a specific building, while the domain name is just the name of the street it's on. Here's how they break down:
- Domain Name: The core identifier for your website.
- URL: Contains additional information such as:
- Protocol: Indicates how your browser should communicate with the web server (e.g., 'https://'). 'HTTPS' ensures a secure connection, encrypting data transmitted between your browser and the website.
- Subdomain: A prefix to the domain name (e.g., 'www'). While 'WWW' used to be standard, it's now often optional.
- Path: Specifies the exact location of a specific page or resource on the server (e.g., '/blog/how-to-choose-a-domain-name'). The path directs the server to the specific file or content you want to access.
- Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN): The complete domain name, including the hostname (e.g., 'www.example.com'). The FQDN helps the DNS accurately locate the web server.
So, while a domain name is a crucial part of a URL, it's not the whole story. A URL provides all the necessary information for your browser to find and display a specific web page or resource.
For example:
- Domain Name: businessnamegenerator.com
- Fully Qualified Domain Name: www.businessnamegenerator.com
- URL: https://www.businessnamegenerator.com/what-is-a-domain-name/
Understanding the distinction between domain names and URLs helps you navigate the web with greater clarity and appreciate the intricacies of web addressing.
Choosing the Right Domain Name
Tips for Selecting a Great Domain Name
Choosing the perfect domain name is vital for building a strong online presence. A well-chosen domain can boost your brand, improve your SEO, and make it easier for customers to find you. Here are some tips to help you make the right choice:
- Keep it Short and Memorable: Shorter domain names are easier to remember and type. Aim for a name that's concise and catchy to stick in people's minds.
- Use Relevant Keywords: Incorporate keywords related to your business or website into your domain name. This can enhance your search engine ranking and help potential customers understand what your site is about.
- Choose the Right Extension: '.com' is the most common and widely recognized extension, but consider others like '.net,' '.org,' or industry-specific extensions if they better suit your needs.
- Make it Easy to Spell and Pronounce: Avoid unusual spellings or words that are hard to pronounce. A domain name that's easy to say and spell reduces the chances of typos and makes it easier for people to share your website.
- Check for Availability: Before settling on a domain name, ensure it's available. Use a domain name registrar to check if the name is already registered.
- Consider Your Brand: Your domain name should reflect your brand identity and values. Choose a name that aligns with your business name, logo, and overall brand messaging.
- Avoid Hyphens and Numbers: Hyphens and numbers can make your domain name harder to remember and type. It's generally best to avoid them unless they're essential to your brand.
- Protect Your Brand: Register variations of your domain name to prevent competitors from using similar names. This includes registering different extensions and common misspellings of your domain name.
By following these tips, you can select a domain name that sets your website up for success. A strong domain name is a valuable asset that can enhance your online visibility, brand recognition, and overall business growth.
Using Business Name Generator to Find a Domain Name
Steps to Generate and Select a Domain Name
Business Name Generator isn't just for finding business names; it can also help you discover available domain names related to your business idea. Here's how to use it:
- Enter Keywords: Start by entering keywords related to your business or website into the Business Name Generator search bar.
- Generate Names: Click the 'Generate' button to produce a list of potential business names and domain name suggestions.
- Filter Results: Use the filters to narrow down the results based on your preferences, such as length, style, and industry.
- Check Availability: Once you find a name you like, check its domain name availability. Business Name Generator often provides domain availability checks directly within the search results.
- Refine Your Search: If your initial search doesn't yield the perfect result, try different keywords or filters to refine your search.
- Register Your Domain: Once you find an available domain name that aligns with your brand, register it through a reputable domain name registrar.
Business Name Generator simplifies the domain name search process, helping you brainstorm ideas and quickly assess availability. It's a valuable tool for anyone starting an online business or launching a new website.
Pros and Cons of Using Business Name Generator
Pros:
- Provides a wide range of name suggestions.
- Helps with brainstorming creative business and domain names.
- Often includes domain availability checks.
- User-friendly interface for easy navigation.
- Saves time compared to manual brainstorming.
Cons:
- Some suggestions may not be relevant to your specific business.
- The best names may already be taken.
- Can generate generic names that lack originality.
- Domain availability checks may not always be accurate.
- Relies on keyword input, which may limit creativity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What if my desired .com domain name is already taken?
If your first choice for a .com domain is unavailable, don't worry. You have several options:
- Consider Alternative Extensions: Explore other domain extensions like .net, .org, .info, .biz, or country-specific extensions (e.g., .ca for Canada, .uk for the United Kingdom). Some of these extensions may be available and still suitable for your website.
- Get Creative with the Name: Try adding a word or phrase to your desired domain name to make it unique. For example, if 'example.com' is taken, try 'getexample.com' or 'exampleonline.com.'
- Negotiate with the Owner: If you're set on a specific domain name, you can try to contact the current owner and offer to buy it. Domain name brokers can help facilitate this process.
- Consider a Different Name: If all else fails, it might be best to choose a completely different domain name that's available and aligns with your brand. Remember to prioritize brand relevance and memorability when considering alternatives.
How much does a domain name typically cost?
The cost of a domain name can vary depending on several factors, including:
- Extension: .com domains are often priced higher than less common extensions.
- Registrar: Different domain name registrars may offer different prices.
- Registration Period: Most registrars offer discounts for longer registration periods (e.g., multiple years).
- Domain Privacy: Adding domain privacy protection can increase the cost.
- Premium Domains: Some domain names are considered 'premium' and can command much higher prices.
Typically, you can expect to pay anywhere from $10 to $20 per year for a standard .com domain name. However, premium domains can cost hundreds or even thousands of dollars. It's important to compare prices from different registrars and consider the additional services offered.
Do I need web hosting to have a domain name?
Yes, you typically need web hosting to make your website accessible online. Here's why:
- Domain Name: Your domain name is your website's address. It tells people how to find you.
- Web Hosting: Web hosting is where your website's files are stored. It's the physical location of your website on the internet.
Think of your domain name as your street address and web hosting as the actual building on that street. Without a building (web hosting), there's nowhere for people to visit even if they have your address (domain name). When someone types your domain name into their browser, the DNS directs them to the web server hosting your website's files. If you don't have web hosting, there's no server to respond to the request, and your website won't be accessible.
Related Questions
How do I transfer a domain name from one registrar to another?
Transferring a domain name involves moving the registration of your domain from one domain registrar to another. Here's a general outline of the process:
- Unlock Your Domain: Log in to your current domain registrar and unlock your domain name. This prevents unauthorized transfers.
- Obtain an Authorization Code (EPP Code): Request an authorization code (also known as an EPP code or transfer code) from your current registrar. This code is required to initiate the transfer.
- Initiate the Transfer with the New Registrar: Go to the website of your new domain registrar and initiate the domain transfer process. You'll need to provide the domain name and authorization code.
- Approve the Transfer: Your current registrar will send you an email asking you to approve the transfer. Follow the instructions in the email to confirm the transfer.
- Wait for the Transfer to Complete: The transfer process typically takes 5-7 days to complete. During this time, your website should remain accessible.
It's important to note that you may need to wait at least 60 days after registering or transferring a domain name before you can transfer it again. Also, ensure that your domain name is not expired or close to expiring before initiating the transfer.
 Pickaxe: Monetize AI Tools Without Coding in 2025
Exploring Pickaxe: The Future of No-Code AI Development?The world of AI tool development is constantly evolving, and Pickaxe is making a significant impact by allowing users to create, deploy, and monetize AI-powered tools without any coding knowledge. Is this the future we're heading towards for no
Pickaxe: Monetize AI Tools Without Coding in 2025
Exploring Pickaxe: The Future of No-Code AI Development?The world of AI tool development is constantly evolving, and Pickaxe is making a significant impact by allowing users to create, deploy, and monetize AI-powered tools without any coding knowledge. Is this the future we're heading towards for no
 Future-Proof Your UX Career: Essential Skills for Success in 2025
In the ever-changing world of UX and product design, it's clear that the field isn't dying—it's transforming. To stay ahead, designers must focus on key growth areas to remain competitive. As AI and automation reshape how we design, it's essential to evolve from just being creators to becoming curat
Future-Proof Your UX Career: Essential Skills for Success in 2025
In the ever-changing world of UX and product design, it's clear that the field isn't dying—it's transforming. To stay ahead, designers must focus on key growth areas to remain competitive. As AI and automation reshape how we design, it's essential to evolve from just being creators to becoming curat
 How AI will transform cybersecurity in 2025 - and supercharge cybercrime
The cybersecurity landscape in 2024 was rocked by severe ransomware attacks, AI-driven social engineering, and state-sponsored cyber operations that racked up billions in damages. As we step into 2025, the mix of AI advancements, geopolitical tensions, and increasingly complex attack surfaces is set
How AI will transform cybersecurity in 2025 - and supercharge cybercrime
The cybersecurity landscape in 2024 was rocked by severe ransomware attacks, AI-driven social engineering, and state-sponsored cyber operations that racked up billions in damages. As we step into 2025, the mix of AI advancements, geopolitical tensions, and increasingly complex attack surfaces is set