Business Intelligence vs. Data Analytics: Understanding the Core Differences
While business intelligence (BI) and data analytics (DA) are frequently mentioned together, they serve distinct purposes in data-driven organizations. This guide clearly differentiates these critical disciplines, examining their unique contributions to corporate strategy and operational excellence. We'll explore how mastering both approaches enables businesses to achieve higher data maturity and sustainable competitive advantages.
Key Points
BI and DA specialists collaboratively enable data-informed business decisions
Advanced data maturity unlocks transformative organizational insights
BI centers on developing interactive dashboards for ongoing performance tracking
DA specializes in investigating historical data patterns and trends
BI practitioners require balanced technical and interpersonal capabilities
Continuous monitoring represents a vital BI implementation phase
Understanding Business Intelligence (BI) and Data Analytics (DA)
What is Data Maturity?
Data maturity has become a strategic imperative for modern enterprises seeking to maximize their information assets' value. This framework assesses an organization's ability to transform raw data into strategic insights that drive measurable business outcomes.

Four pillars support robust data maturity:
- Data Quality: Maintaining accuracy, consistency and reliability throughout the data lifecycle
- Data Accessibility: Ensuring seamless availability across operational units
- Data Literacy: Building organizational competency in data interpretation
- Data Governance: Implementing compliant, ethical data management protocols
The Role of BI and DA Professionals
BI and DA teams combine complementary expertise to create comprehensive data solutions. Analysts focus on retrospective examination, answering critical "what happened" questions through historical data investigation. BI experts take this foundation further, developing forward-looking reporting frameworks that illuminate "what might happen" scenarios.
BI builds vital monitoring mechanisms that track key business metrics through reproducible processes, including:
- New business pipeline progression
- Customer acquisition trends
- Marketing campaign performance
This continuous insight generation enables leaders to make timely, impactful business decisions.
Tool Building and Practicality
The interplay between BI and DA manifests most clearly in their tool development and application approaches. BI architects create the essential data infrastructure—ETL pipelines, data models, and visualization dashboards—that turns organizational data into accessible business intelligence.

DA practitioners then leverage these BI-created resources to conduct targeted investigations, applying specialized analytical methodologies to solve specific business challenges.
Levels of Business Intelligence
Capture: Building the Data Foundation
Organizations establish their data architecture during the foundational Capture phase. This critical first step involves:
- Identifying relevant internal and external data sources
- Implementing secure, scalable storage solutions
- Developing rigorous data validation procedures
Analyze: Uncovering Hidden Patterns
The Analyze level reveals meaningful business insights through advanced techniques including:
- Predictive modeling and statistical analysis
- Interactive data visualization
- Strategic reporting frameworks
Monitor: Real-Time Awareness for Agile Decisions
Mature BI environments implement dynamic monitoring systems featuring:
- Executive dashboards tracking KPIs in real-time
- Automated anomaly detection alerts
- Continuous performance benchmarking
Technical and Professional Skills for BI
Leveraging Technical Expertise
Successful BI practitioners master core technical competencies including:
- Enterprise-scale database administration
- Advanced SQL query development
- Data visualization best practices

Cultivating Professional Skillsets
Top BI professionals complement technical skills with essential business capabilities:
- Stakeholder engagement and communication
- Project prioritization and management
- Business process optimization
Business Intelligence Platform: Comparing Pricing Structures
Exploring Popular Options and Costs
Platform Pricing Model Key Considerations Tableau Subscription-based (per user/month) Excellent visualization capabilities; wide range of integrations; may be expensive for large teams. Power BI Subscription-based (per user/month) Integrates seamlessly with Microsoft ecosystem; strong self-service features; complex data modeling can be challenging. Looker Custom pricing (based on data volume) Flexible data modeling; strong collaboration features; requires technical expertise for setup and maintenance. Qlik Sense Subscription-based (per user/month) Associative data engine; AI-powered analytics; can be complex to learn and implement.
Pros and Cons of Business Intelligence
Pros
- Enhanced strategic decision-making velocity
- Increased operational efficiency
- Improved customer intelligence
- New revenue stream identification
Cons
- Significant initial implementation investment
- Specialized talent requirements
- Data security management complexity
- Organizational change management challenges
Key Features of Business Intelligence Platforms
Essential Components for Data-Driven Success
Comprehensive BI solutions should include:
- Interactive data visualization tools
- Automated reporting capabilities
- Predictive analytics functionality
- Customizable executive dashboards
Use Cases: Where Business Intelligence Thrives
Real-World Examples of BI in Action
Modern enterprises across industries leverage BI to:
- Optimize supply chain operations
- Personalize customer experiences
- Identify emerging market opportunities
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the primary goal of business intelligence?
BI transforms organizational data into actionable intelligence that informs strategic planning and tactical decision-making, enabling continuous business improvement.
How does data maturity impact the effectiveness of business intelligence?
High data maturity ensures reliable, accessible data assets that BI systems can effectively transform into impactful business insights and recommendations.
Related Questions
How can businesses effectively monitor their data and respond to changing conditions?
Leading organizations implement real-time monitoring systems that track critical KPIs through automated dashboards and alerts, enabling rapid response to emerging opportunities or challenges.
Related article
 Amazon introduces AI-powered Lens Live for real-world shopping experiences
Amazon continues advancing AI-powered shopping innovations with Tuesday's introduction of Lens Live, an enhanced version of its visual search technology that gives customers real-time product discovery capabilities. This upgrade builds upon Amazon Le
Amazon introduces AI-powered Lens Live for real-world shopping experiences
Amazon continues advancing AI-powered shopping innovations with Tuesday's introduction of Lens Live, an enhanced version of its visual search technology that gives customers real-time product discovery capabilities. This upgrade builds upon Amazon Le
 "AI Mode Introduces Innovative Ways to Engage with Information"
The Future of AI-Powered Search Is Here: AI Mode Opens to EveryoneMillions of users are revolutionizing their search experience with AI Mode in Google Labs - tackling complex inquiries, refining results through conversational follow-ups, and uncoveri
"AI Mode Introduces Innovative Ways to Engage with Information"
The Future of AI-Powered Search Is Here: AI Mode Opens to EveryoneMillions of users are revolutionizing their search experience with AI Mode in Google Labs - tackling complex inquiries, refining results through conversational follow-ups, and uncoveri
 Easily Create Stunning Comics with AI-Powered Comic Factory
Comic Factory AI represents a quantum leap in digital storytelling, transforming how visual narratives are crafted. This groundbreaking platform leverages artificial intelligence to instantly convert text descriptions into professional-grade comic ar
Comments (0)
0/200
Easily Create Stunning Comics with AI-Powered Comic Factory
Comic Factory AI represents a quantum leap in digital storytelling, transforming how visual narratives are crafted. This groundbreaking platform leverages artificial intelligence to instantly convert text descriptions into professional-grade comic ar
Comments (0)
0/200
While business intelligence (BI) and data analytics (DA) are frequently mentioned together, they serve distinct purposes in data-driven organizations. This guide clearly differentiates these critical disciplines, examining their unique contributions to corporate strategy and operational excellence. We'll explore how mastering both approaches enables businesses to achieve higher data maturity and sustainable competitive advantages.
Key Points
BI and DA specialists collaboratively enable data-informed business decisions
Advanced data maturity unlocks transformative organizational insights
BI centers on developing interactive dashboards for ongoing performance tracking
DA specializes in investigating historical data patterns and trends
BI practitioners require balanced technical and interpersonal capabilities
Continuous monitoring represents a vital BI implementation phase
Understanding Business Intelligence (BI) and Data Analytics (DA)
What is Data Maturity?
Data maturity has become a strategic imperative for modern enterprises seeking to maximize their information assets' value. This framework assesses an organization's ability to transform raw data into strategic insights that drive measurable business outcomes.

Four pillars support robust data maturity:
- Data Quality: Maintaining accuracy, consistency and reliability throughout the data lifecycle
- Data Accessibility: Ensuring seamless availability across operational units
- Data Literacy: Building organizational competency in data interpretation
- Data Governance: Implementing compliant, ethical data management protocols
The Role of BI and DA Professionals
BI and DA teams combine complementary expertise to create comprehensive data solutions. Analysts focus on retrospective examination, answering critical "what happened" questions through historical data investigation. BI experts take this foundation further, developing forward-looking reporting frameworks that illuminate "what might happen" scenarios.
BI builds vital monitoring mechanisms that track key business metrics through reproducible processes, including:
- New business pipeline progression
- Customer acquisition trends
- Marketing campaign performance
This continuous insight generation enables leaders to make timely, impactful business decisions.
Tool Building and Practicality
The interplay between BI and DA manifests most clearly in their tool development and application approaches. BI architects create the essential data infrastructure—ETL pipelines, data models, and visualization dashboards—that turns organizational data into accessible business intelligence.

DA practitioners then leverage these BI-created resources to conduct targeted investigations, applying specialized analytical methodologies to solve specific business challenges.
Levels of Business Intelligence
Capture: Building the Data Foundation
Organizations establish their data architecture during the foundational Capture phase. This critical first step involves:
- Identifying relevant internal and external data sources
- Implementing secure, scalable storage solutions
- Developing rigorous data validation procedures
Analyze: Uncovering Hidden Patterns
The Analyze level reveals meaningful business insights through advanced techniques including:
- Predictive modeling and statistical analysis
- Interactive data visualization
- Strategic reporting frameworks
Monitor: Real-Time Awareness for Agile Decisions
Mature BI environments implement dynamic monitoring systems featuring:
- Executive dashboards tracking KPIs in real-time
- Automated anomaly detection alerts
- Continuous performance benchmarking
Technical and Professional Skills for BI
Leveraging Technical Expertise
Successful BI practitioners master core technical competencies including:
- Enterprise-scale database administration
- Advanced SQL query development
- Data visualization best practices

Cultivating Professional Skillsets
Top BI professionals complement technical skills with essential business capabilities:
- Stakeholder engagement and communication
- Project prioritization and management
- Business process optimization
Business Intelligence Platform: Comparing Pricing Structures
Exploring Popular Options and Costs
| Platform | Pricing Model | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Tableau | Subscription-based (per user/month) | Excellent visualization capabilities; wide range of integrations; may be expensive for large teams. |
| Power BI | Subscription-based (per user/month) | Integrates seamlessly with Microsoft ecosystem; strong self-service features; complex data modeling can be challenging. |
| Looker | Custom pricing (based on data volume) | Flexible data modeling; strong collaboration features; requires technical expertise for setup and maintenance. |
| Qlik Sense | Subscription-based (per user/month) | Associative data engine; AI-powered analytics; can be complex to learn and implement. |
Pros and Cons of Business Intelligence
Pros
- Enhanced strategic decision-making velocity
- Increased operational efficiency
- Improved customer intelligence
- New revenue stream identification
Cons
- Significant initial implementation investment
- Specialized talent requirements
- Data security management complexity
- Organizational change management challenges
Key Features of Business Intelligence Platforms
Essential Components for Data-Driven Success
Comprehensive BI solutions should include:
- Interactive data visualization tools
- Automated reporting capabilities
- Predictive analytics functionality
- Customizable executive dashboards
Use Cases: Where Business Intelligence Thrives
Real-World Examples of BI in Action
Modern enterprises across industries leverage BI to:
- Optimize supply chain operations
- Personalize customer experiences
- Identify emerging market opportunities
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the primary goal of business intelligence?
BI transforms organizational data into actionable intelligence that informs strategic planning and tactical decision-making, enabling continuous business improvement.
How does data maturity impact the effectiveness of business intelligence?
High data maturity ensures reliable, accessible data assets that BI systems can effectively transform into impactful business insights and recommendations.
Related Questions
How can businesses effectively monitor their data and respond to changing conditions?
Leading organizations implement real-time monitoring systems that track critical KPIs through automated dashboards and alerts, enabling rapid response to emerging opportunities or challenges.
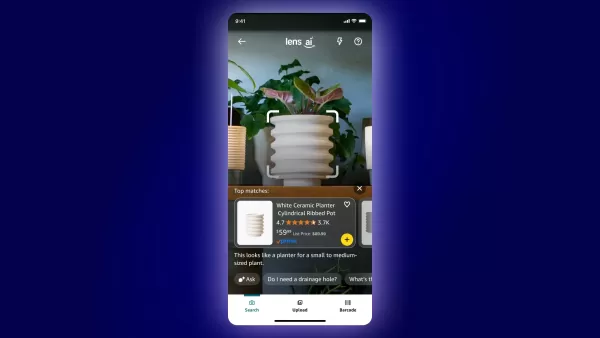 Amazon introduces AI-powered Lens Live for real-world shopping experiences
Amazon continues advancing AI-powered shopping innovations with Tuesday's introduction of Lens Live, an enhanced version of its visual search technology that gives customers real-time product discovery capabilities. This upgrade builds upon Amazon Le
Amazon introduces AI-powered Lens Live for real-world shopping experiences
Amazon continues advancing AI-powered shopping innovations with Tuesday's introduction of Lens Live, an enhanced version of its visual search technology that gives customers real-time product discovery capabilities. This upgrade builds upon Amazon Le
 "AI Mode Introduces Innovative Ways to Engage with Information"
The Future of AI-Powered Search Is Here: AI Mode Opens to EveryoneMillions of users are revolutionizing their search experience with AI Mode in Google Labs - tackling complex inquiries, refining results through conversational follow-ups, and uncoveri
"AI Mode Introduces Innovative Ways to Engage with Information"
The Future of AI-Powered Search Is Here: AI Mode Opens to EveryoneMillions of users are revolutionizing their search experience with AI Mode in Google Labs - tackling complex inquiries, refining results through conversational follow-ups, and uncoveri
 Easily Create Stunning Comics with AI-Powered Comic Factory
Comic Factory AI represents a quantum leap in digital storytelling, transforming how visual narratives are crafted. This groundbreaking platform leverages artificial intelligence to instantly convert text descriptions into professional-grade comic ar
Easily Create Stunning Comics with AI-Powered Comic Factory
Comic Factory AI represents a quantum leap in digital storytelling, transforming how visual narratives are crafted. This groundbreaking platform leverages artificial intelligence to instantly convert text descriptions into professional-grade comic ar